NAS Private Deployment
NAS (Network Attached Storage) is a small server dedicated to file management — it mounts disks on the local network and provides file access, backups, sharing, versioned snapshots, media services, etc. It is not intended for running general compute tasks.
Common NAS vendors:
- Synology
- Lenovo Personal Cloud / ZhiKong / Ugreen
- Western Digital My Cloud
- ...
No domain required — private deployment
Local NAS deployment video
The video demonstrates obtaining the deployment script from VoceChat embedded VoceSpace and deploying with it.
If you only want to deploy VoceSpace, download the deployment script and follow the "Manual script deployment" section below.
Download the deployment script
Click to download the shell script below:
Script summary:
- Pulls all required Docker images
- Automatically creates containers
- Does not configure proxy
Manual script deployment
You don't need to modify anything — run the script directly:
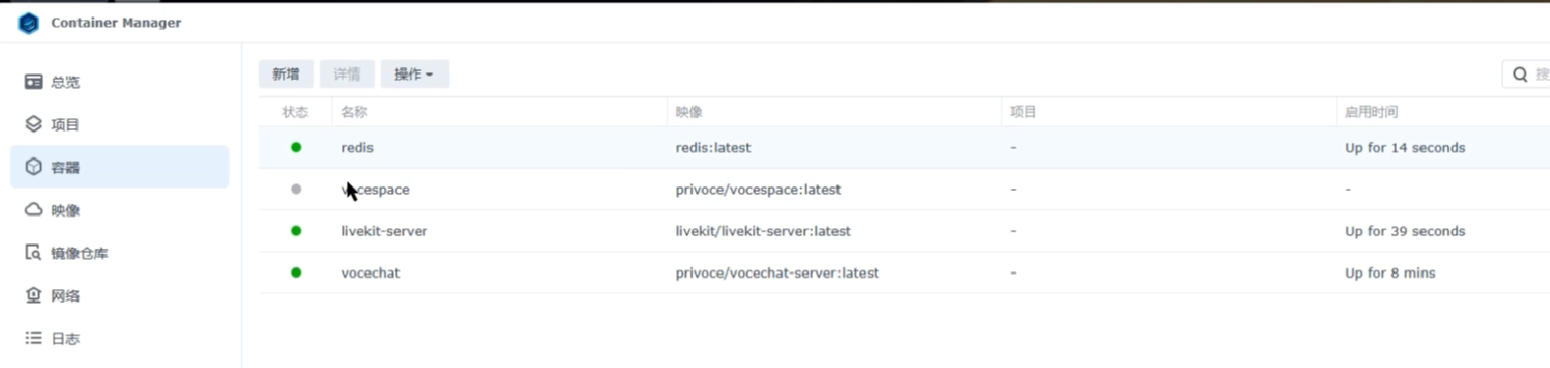
After completion you should see these containers running:
- redis
- vocespace
- livekit-server
Note: the vocespace container may fail to start because vocespace.conf.json lacks read/write permissions.
Add read/write permission for vocespace.conf.json
vocespace.conf.json is located where you ran the script. If you check the container logs you'll likely see: /app/vocespace.conf.json: Permission denied
After granting permission, restart the vocespace container.
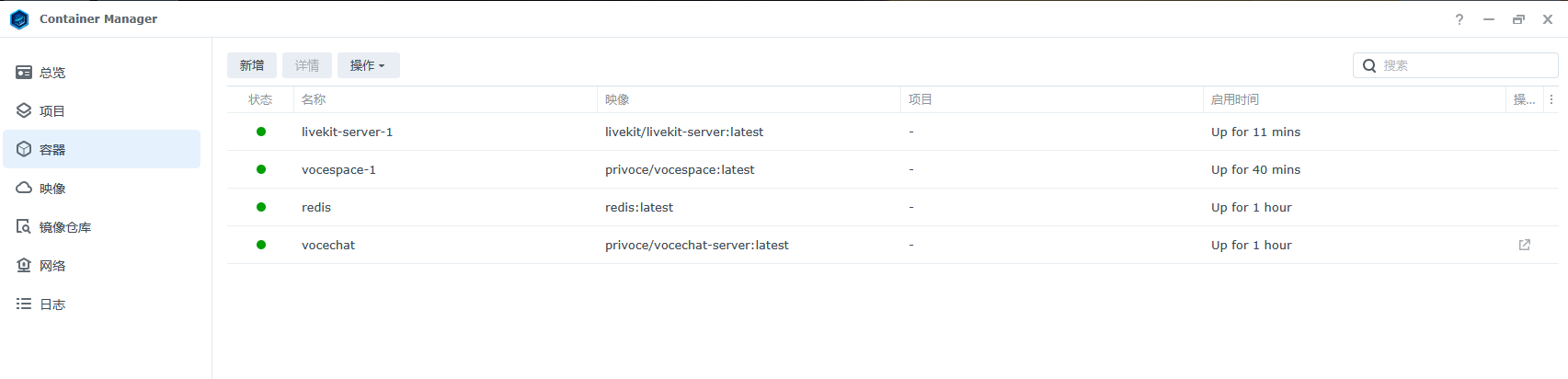
LAN access
At this point your local installation should be complete and containers running, but the service still uses http and ws, which won't work for secure communications. Let's continue.
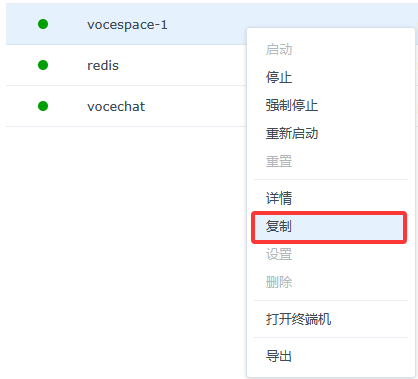
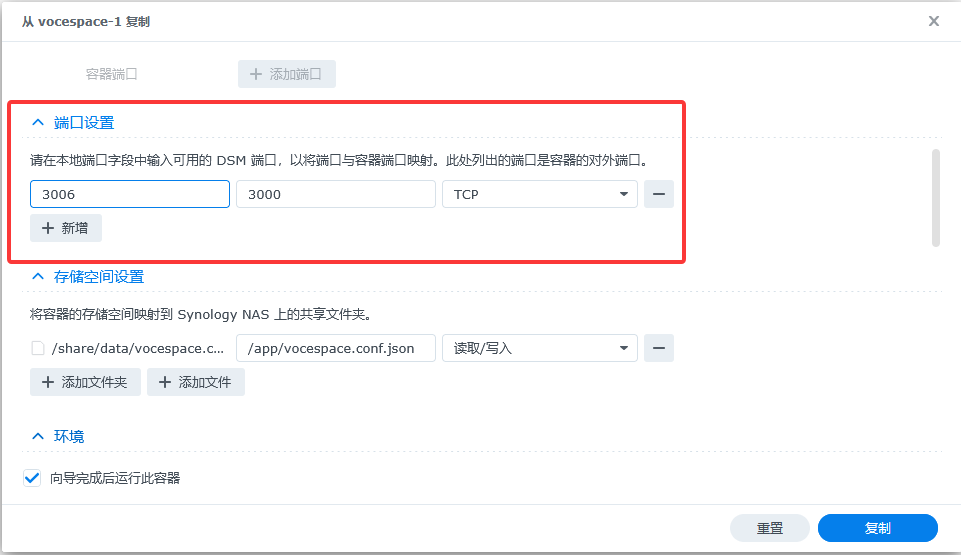
Duplicate the VoceSpace container
Right-click the vocespace container and choose "Duplicate" to create a new instance. Change the original port mapping of 3008 to 3006 (or any other unused port except 3008).
Duplicate the livekit-server container
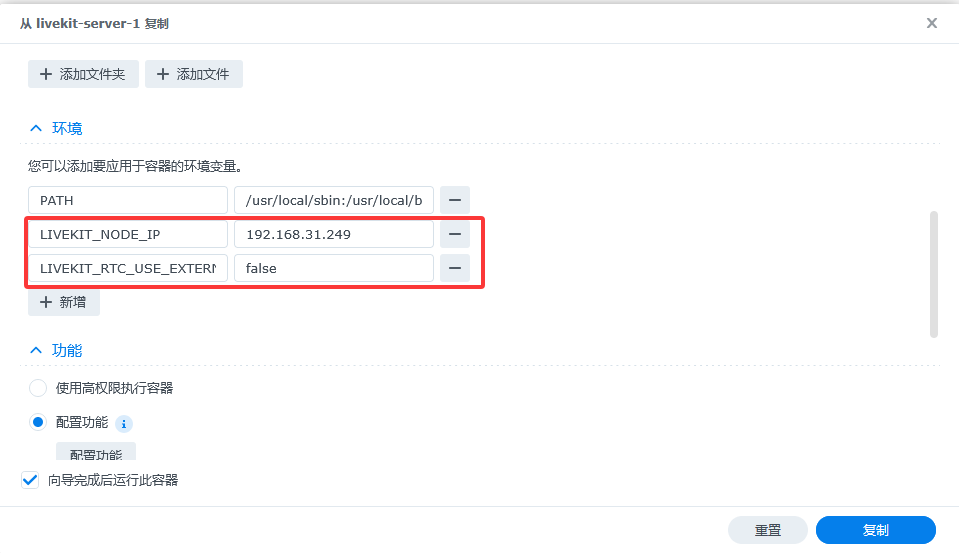
Also duplicate livekit-server. Add the following two environment variables so WebRTC won't route through the public internet. Make sure to use your NAS IP exactly.
LIVEKIT_NODE_IP = your.nas.server.ipLIVEKIT_RTC_USE_EXTERNAL_IP = false
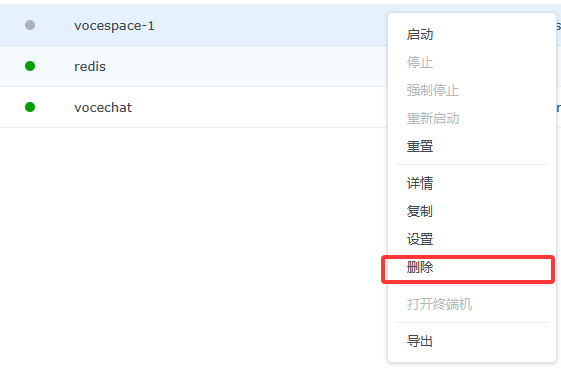
Remove the previous containers
After duplication you can remove the original VoceSpace and livekit-server containers.
Configure Nginx reverse proxy
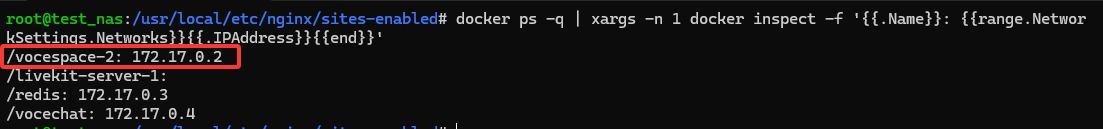
Find VoceSpace IP inside Docker
Run the command below to list all containers' IPs and find the VoceSpace container IP — remember it.
Configure the proxy
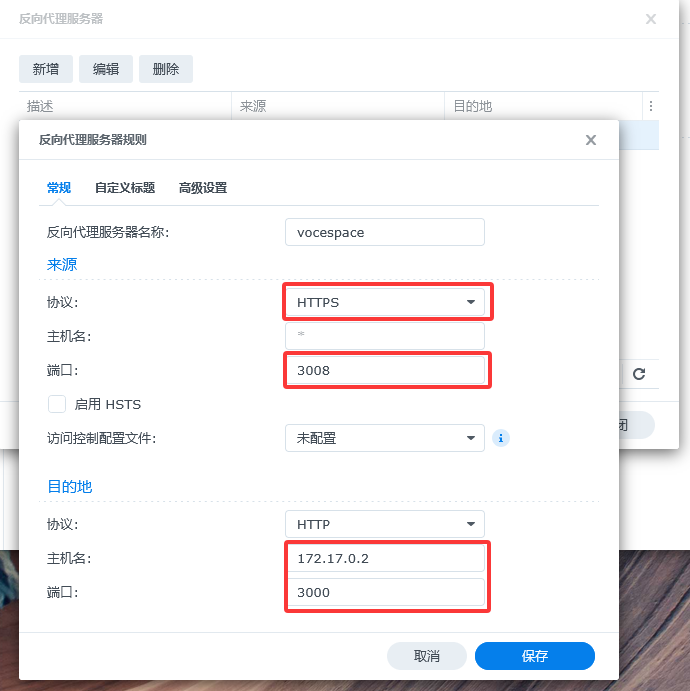
Open Control Panel → Login Portal → Advanced → Reverse Proxy.
Add a new rule and save.
- Source
- Protocol: HTTPS
- Hostname: (leave blank)
- Port: 3008
- Destination
- Protocol: HTTP
- Hostname: (this is the VoceSpace Docker IP)
- Port: 3000
Add RTC configuration
Now modify the Nginx config to upgrade ws to wss for RTC.
The file should look like this when opened:
Insert the following block just above location / { to handle RTC upgrade:
After editing, save and exit (ESC then :wq).
The full config becomes:
Reload nginx
Ensure VoceSpace config and restart container
Edit the VoceSpace configuration file and restart the VoceSpace container:
Pay attention to these settings in the config:
- In
livekit, set the URL to:wss://your.server.ip:3008— note the port is3008, not7880. - In
redis, sethostto your server IP.
Example:
After confirming the config, restart the VoceSpace container and log in. If you see the screen below, LAN access is successfully configured.
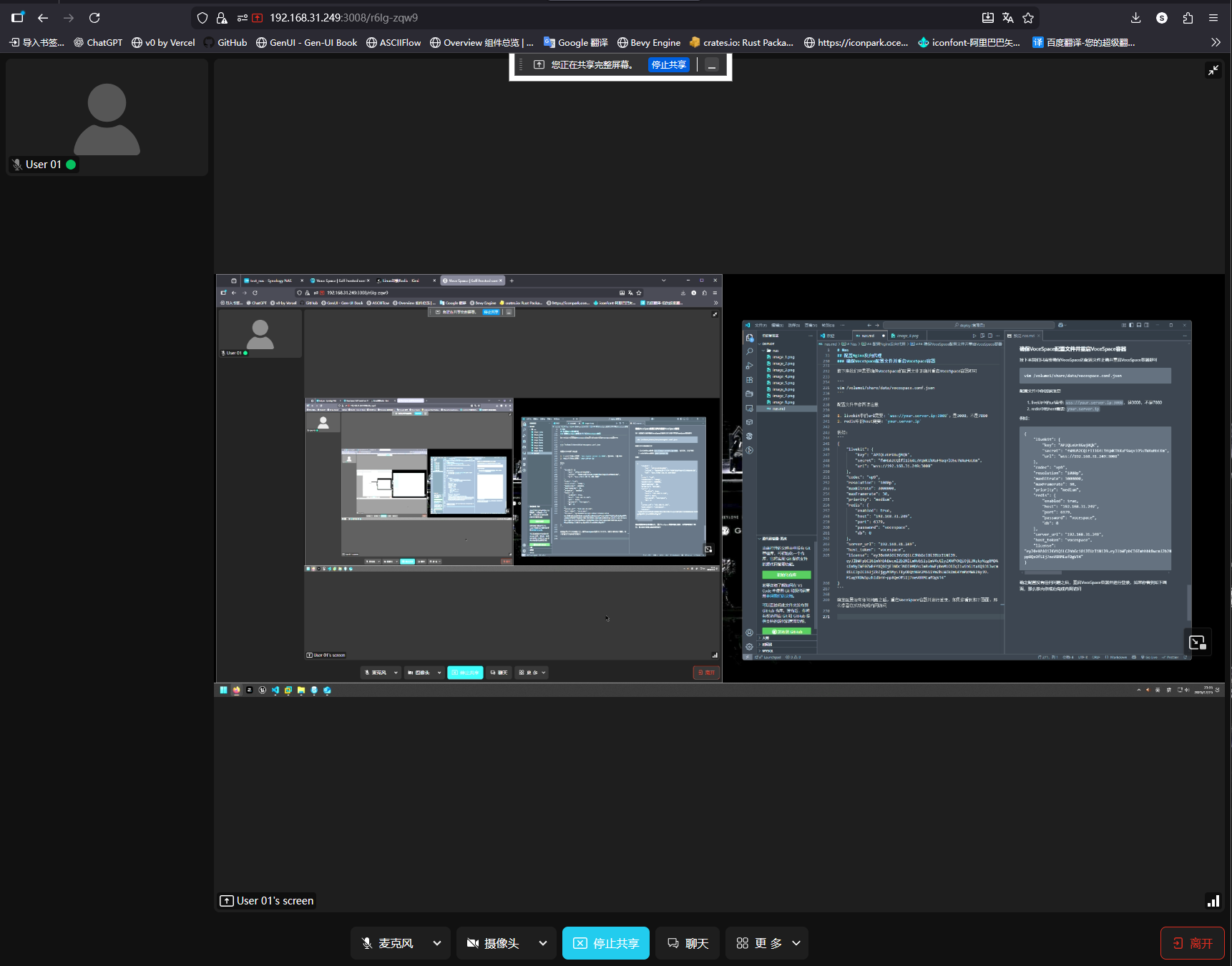
Errors
Restricted RTC Access
Restricted RTC access generally stems from two reasons:
-
Incorrect Vocesspace configuration
-
Inadequate server configuration preventing the service from starting correctly.
To address these issues, consider upgrading the server configuration (minimum 2 cores and 2GB RAM). For configuration problems, check the vocesspace.conf.json file to determine if the livekit.url configuration is incorrect.
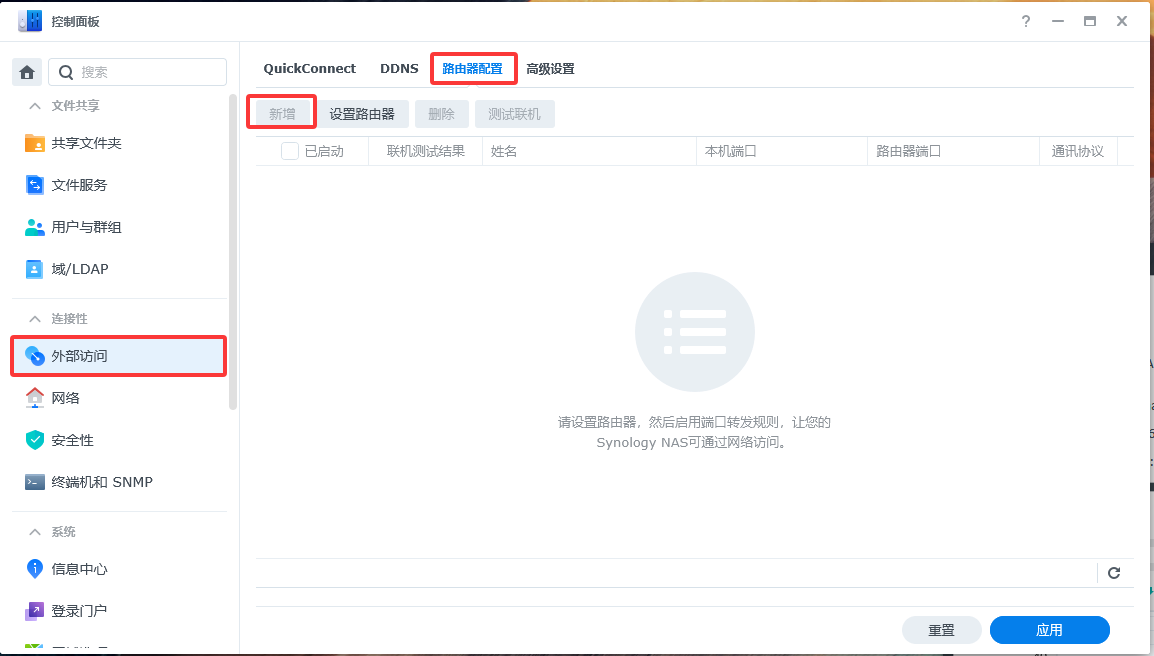
External Port Access
Configuring a router on the NAS may prevent external access. In this case, you need to add port rules.
| port | type | ingress/egress | allow ip |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3008 | tcp | ingress | 0.0.0.0/0 Ipv4 |
| 3008 | tcp | egress | 0.0.0.0/0 Ipv4 |
| 7880 | tcp | ingress | 0.0.0.0/0 Ipv4 |
| 7881 | tcp | ingress | 0.0.0.0/0 Ipv4 |
| 6379 | tcp | ingress | 0.0.0.0/0 Ipv4 |
| 80 | tcp | ingress | 0.0.0.0/0 Ipv4 |
| 443 | tcp | ingress | 0.0.0.0/0 Ipv4 |
| 50000~60000 | udp | ingress | 0.0.0.0/0 Ipv4 |